Timor-Leste officially became ASEAN’s 11th member on 26 October 20251. This milestone opens new opportunities for APAC B2B companies, especially suppliers of machinery, construction and energy systems, logistics providers, and food-processing equipment manufacturers. ASEAN membership brings predictable regulatory frameworks, donor-backed infrastructure pipelines, and easier regional integration. This article outlines the most immediate business opportunities, market realities, and practical market-entry tactics for B2B companies evaluating Timor-Leste in 2025–2030.
What does Timor-Leste’s ASEAN membership mean for APAC businesses?
Becoming the 11th member of ASEAN strengthens regional cooperation and economic integration, signaling a long-term commitment to political and regulatory stability. For B2B companies, ASEAN membership translates into several practical benefits:
Long term
regional mobility
Gradual adoption of ASEAN visa and labor mobility schemes will make it easier for technical experts, engineers, and executives to travel and conduct cross-border projects.
Improved
trade
facilitation
Alignment with ASEAN trade frameworks, customs procedures, and product standards will simplify logistics and documentation.
Access to
funding &
infrastructure programs
Timor-Leste will gain access to ASEAN development funds and donor coordination platforms, creating project pipelines for construction, transport, and energy.
Regulatory stability
&
market access
ASEAN membership signals long-term governance improvement, increasing investor confidence for industrial, logistics, and infrastructure projects.
How large is the market & how does it compare with other ASEAN members?
While Timor-Leste is ASEAN’s smallest economy, its strategic location and ongoing infrastructure development create growing B2B opportunities. The Asian Development Bank (ADB) projects 3.8% economic growth in 2025 and 3.4% in 20262, highlighting its potential as a frontier market for industrial suppliers, infrastructure developers, and logistics providers. Although smaller than Thailand, Vietnam, or Indonesia, Timor-Leste’s import-driven economy and infrastructure demand offer unique entry points for foreign companies.
Key economic indicators in
| Indicator | Timor-Leste | Thailand | Vietnam | Indonesia | Cambodia |
| Nominal GDP (USD) | $2.08B | $514.97B | $433.70B | $1,371.17B | $43.30B |
| GDP per capita (USD) | $1,278 | $7,335 | $4,324 | $4,919 | $2,545 |
| Population (million) | 1.38 | 70.19 | 100.3 | 278.75 | 17.015 |
| FDI inflows (USD) | $205.5M | $18.6B | $36.61B | $47B | $3.96B |
Timor-Leste’s market size is modest, but the concentration of imports in essential goods, capital equipment, and construction materials creates clear opportunities for industrial suppliers.
What this means for B2B and industrial firms?
- Frontier advantage: Timor-Leste’s economy is small, but its import dependency creates steady demand for machinery, vehicles, and industrial systems from road construction to food processing.
- Infrastructure-driven growth: Around 10% of GDP is dedicated to infrastructure, supported by ADB, JICA, and World Bank projects, meaning consistent opportunities for suppliers of equipment, engineering services, and logistics.
- Strategic positioning: ASEAN membership integrates Timor-Leste into regional supply chains, enabling companies to serve the market via hubs in Indonesia or Singapore.
- First-mover potential: Like Cambodia and Laos a decade ago, Timor-Leste is a greenfield market where establishing early partnerships, distributor networks, or public-sector contracts can create long-term value.
Which industries offer the biggest B2B opportunities in 2025?
Energy & power infrastructure
Timor Leste imports refined petroleum valued at approximately US$138 million in 2023 and exports crude petroleum around US$113 million3. This dual dynamic highlights demand for fuel logistics, generation equipment, mini-grid solutions and energy efficiency services.
Opportunities: Suppliers of power generation modules, fuel storage tanks, O&M services, solar + battery systems.
Infrastructure & construction
Donor-funded and government-led infrastructure programmes are active in roads, ports, airports and public facilities. Heavy machinery and construction materials imports are high.
Opportunities: Earth-moving equipment, mobile cranes, building material supply, EPC contracts for public infrastructure.
Industrial machinery & food-processing equipment
With high dependence on imports of machinery and processed foods, and an expanding specialty coffee export sector, there is direct demand for processing, packaging, and cold chain systems.
Opportunities: Turnkey food/ingredient processing lines, bakery equipment, packaging machines, industrial refrigeration & warehousing.
Agriculture value chain & specialty exports
Coffee exports approximate US$19 million and represent about 11 % of total exports4. This creates room for upstream processing, quality certification, export-logistics and packaging.
Opportunities: Roasting lines, sorting and grading equipment, speciality packaging, export supply-chain management.
Logistics, warehousing & customs services
Island geography, limited infrastructure and reliance on imports via main ports mean logistics services are essential.
Opportunities: Freight forwarding specialists, bonded warehousing, temperature-controlled storage, customs brokerage and supply-chain integration for APAC suppliers.
What are Timor-Leste’s key imports and exports?
Timor-Leste’s trade profile in 20235 reflects its import-dependent economy and emerging specialty exports, offering targeted opportunities for B2B suppliers in machinery, construction, energy, logistics, and coffee value chains.
Imports (Total : $988M)
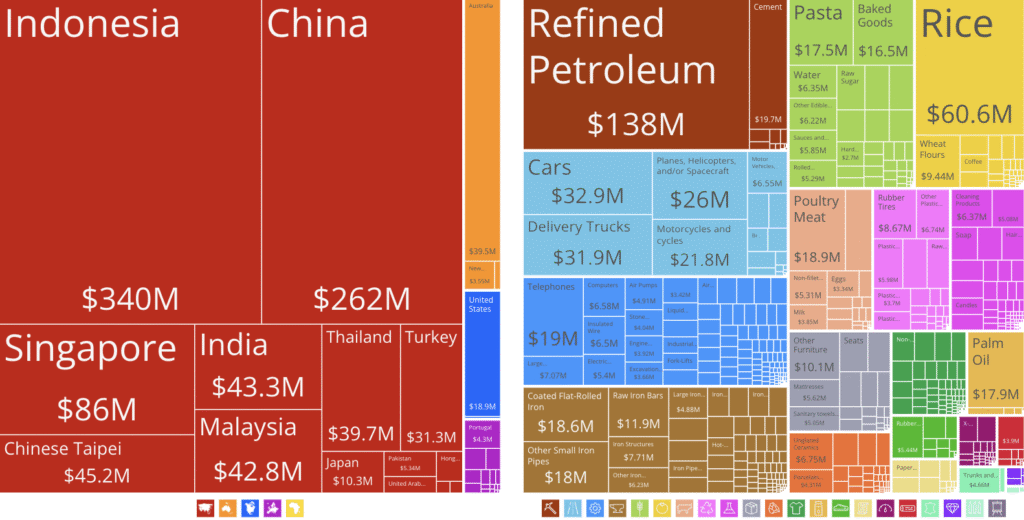
Timor-Leste’s import destinations (2017-2023)
Main sources of imports were:
- Indonesia: US$340 million
- China: US$262 million
- Singapore: US$86 million
- Chinese Taipei: US$45.2 million
- India: US$43.3 million
Timor-Leste’s imported products (2017-2023)
In 2023, Timor-Leste’s top imports were:
- Refined petroleum: US$138 million
- Rice: US$60.6 million
- Cars: US$32.9 million
- Delivery trucks: US$31.9 million
- Planes, helicopters, and/or spacecraft: US$26 million
Exports (Total : $163M)

Timor-Leste’s export destinations (2017-2023)
Primary export destinations included:
- China: US$74.7 million
- Singapore: US$40.3 million
- Japan: US$23.6 million
- Indonesia: US$8.13 million
- United States: US$4.73 million
Timor-Leste’s exported products (2017-2023)
In 2023, Timor-Leste’s total exports ranked 190 out of 226 economies globally. The top export commodities were
- Crude petroleum: US$113 million
- Petroleum gas: US$22.5 million
- Coffee: US$19.1 million
- Scrap iron: US$909 000
- Telephones: US$664 000
What ASEAN membership changes for B2B trade and mobility (2025–2030)
As Timor-Leste aligns with ASEAN’s Economic Community Blueprint 2025, B2B benefits will evolve through:
- Customs modernization aligned with the ASEAN Single Window system.
- Infrastructure co-financing through the ASEAN Infrastructure Fund and regional development banks.
- Workforce upskilling programs, improving industrial labor availability.
- Digital trade and e-logistics participation, allowing integration into regional supply chains.
These structural shifts mean that manufacturers, EPC contractors, and logistics providers that build early presence will capture long-term returns as the market matures.

Key takeaways
- Timor-Leste is a “greenfield B2B market” with import-dependent demand.
- Infrastructure, energy, and industrial equipment suppliers have early-mover potential.
- ASEAN membership ensures predictable regulations, trade facilitation, and regional integration.
- Coffee and specialty agriculture create niche opportunities for upstream processing and export logistics.
- Early engagement and local partnerships position companies for long-term returns.
Explore our insightful articles on APAC marketing strategies for more insights
- Local SEO for Southeast Asia B2B success
- B2B marketing trends: Essential strategies for manufacturers
- Go-To-Market strategies for success in Southeast Asia
Discover how Reachlane can help you navigate these trends and position your brand for success in APAC.
Last updated
Sources
1. ASEAN Briefing (link to report)
2. Asian Development Bank (ADB) (link to report)
3,4,5 OEC (link to report)


